Chances are that when we phone or text someone, send a video clip or use our computer to log onto a communications network, we dont think much about the underlying network technology we are using. But it has been undergoing constant evolution over the years, and open standards have played a large role in that process.
Open standards have led to interoperability among equipment from different suppliers, enabling network operators to move away from expensive, proprietary solutions. They have also helped make possible a greater use of software-defined networking, where cloud computing, network function virtualization and artificial intelligence (AI) techniques are used to control core network functions, rather than dedicated hardware.
These changes have taken place in phases across the network, and the emphasis to date has been to virtualize the network core and applications.
More recently, however, network operators are looking to virtualize the part of a mobile network known as the radio access network, or RAN. The RAN is the outermost portion of a mobile network, which connects smartphones and other end-user devices to the networks core. However, a move called Open RAN, or O-RAN, is under way to bring the same fundamental changes to the RAN as are being made elsewhere in the network.
To incubate new Open RAN standards and related products and services and complement existing Open-RAN industry efforts, IEEE Standards Association (IEEE SA) has launched a new Open RAN Industry Connections Activity within the Connectivity and Telecom Practice. The new IEEE SA Open RAN Industry Connections Program will facilitate open, inclusive collaboration among organizations and individuals to move this rapidly changing technology forward.
Why is Open RAN Important?
Open RAN architectures will bring about more versatile, flexible, and resilient networks offering new features and capabilities, higher reliability, and greater security. Open RAN will offer network operators savings in operational costs and capital expenses, along with greater ease in implementing orchestration and closed-loop automation at the edge, and other new functions than is possible at present, such as dynamic resource scheduling, embedding detection, and mitigation techniques.
Traditionally, the radio access network has consisted of integrated hardware and software components. But under the Open RAN approach, hardware and software are disaggregated into three main parts:
- a radio unit to send, receive, amplify, and digitize RF signals;
- distributed units; and
- centralized units.
The latter two are the computational parts of a network base station; they send the digitized signals into the network, and their physical locations and configurations can vary to accommodate different system designs.
Open RAN opens the protocols and interfaces among these RAN building blocks. This disaggregation of hardware and software benefits operators by allowing multi-vendor deployments, which reduce costs by encouraging competition and enable smaller suppliers to become part of the development ecosystem for 5G communications and beyond.
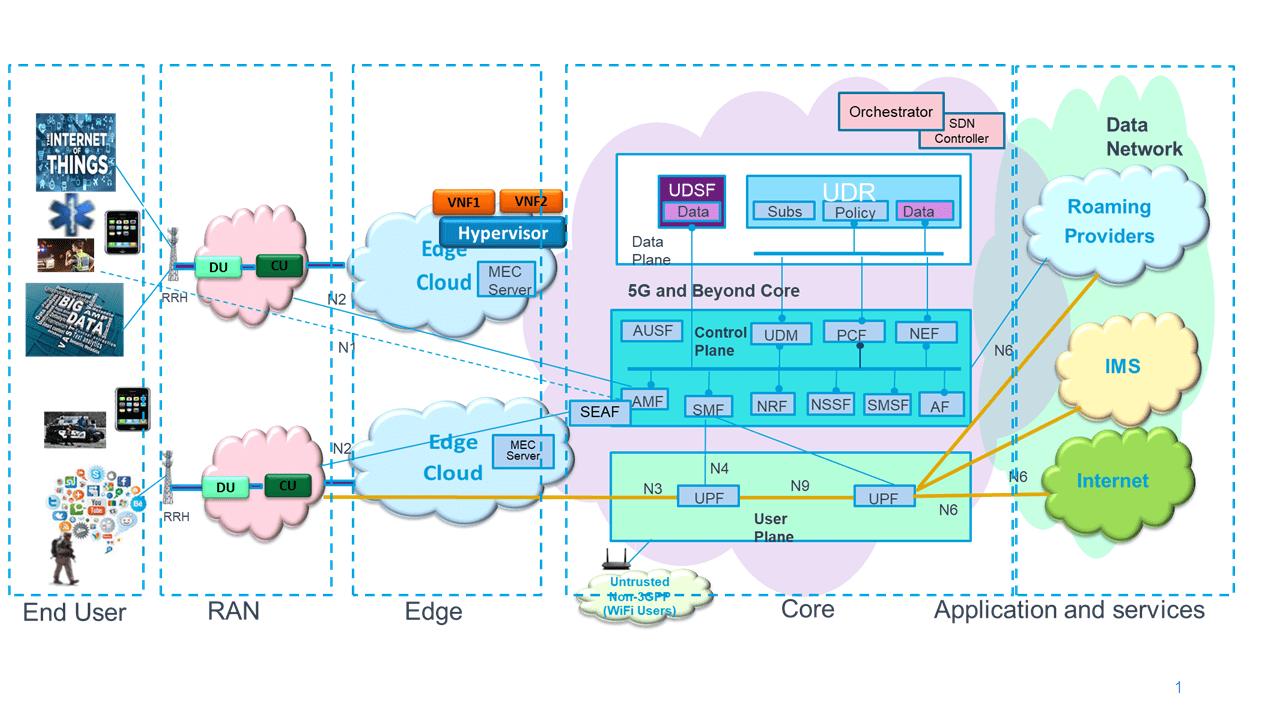
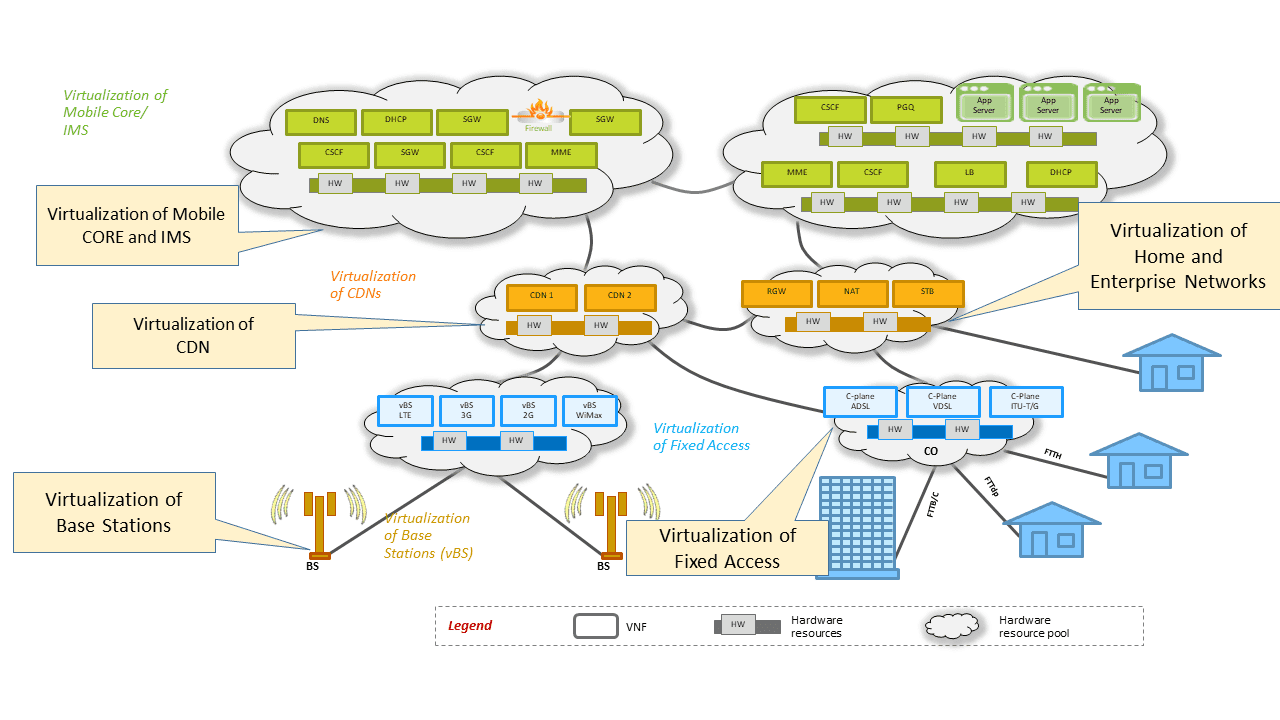
In addition, Open RAN makes use of cloud computing to implement sophisticated network function virtualization (NFV) and AI capabilities. NFV is used to create virtual versions of a RAN for greater flexibility in network management and to provide new functionalities and services quickly and easily. AI, meanwhile, is used to run increasingly sophisticated algorithms for faster, better network performance, most notably at the edge of the network, where it offers the advantages of low latency and a local decision-making capability.
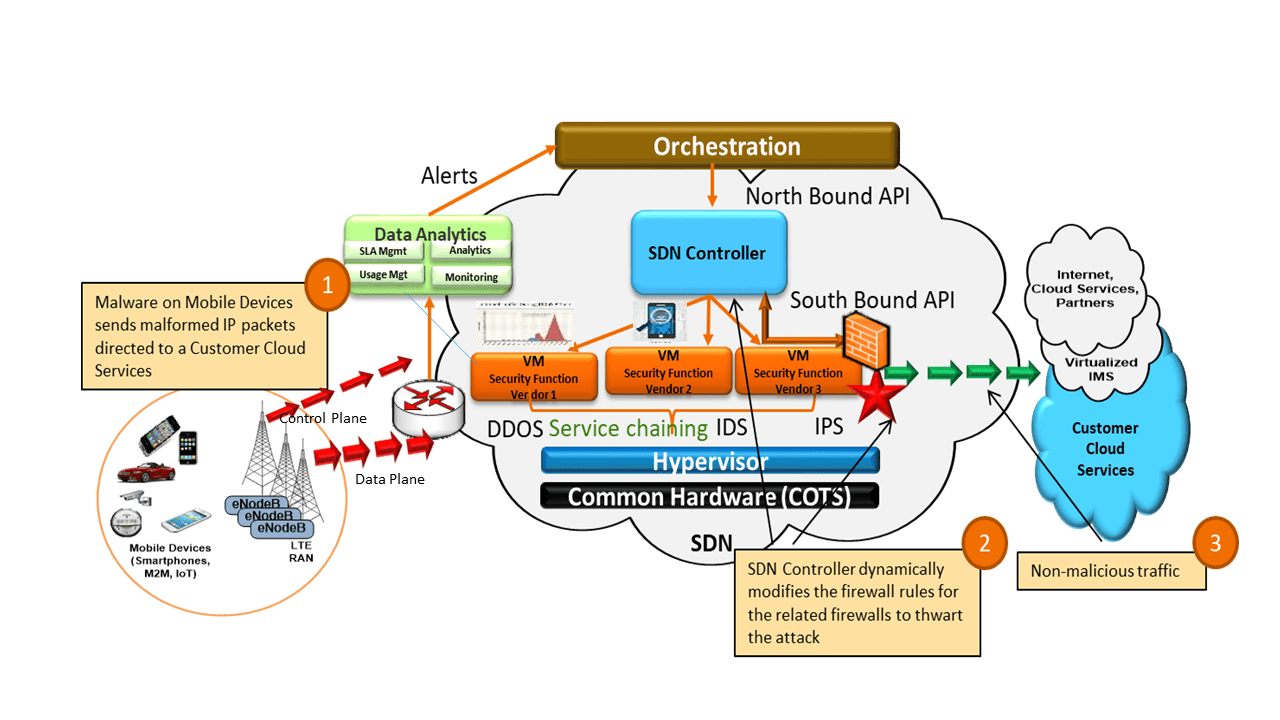
For example, network security is one area where Open RAN is expected to make a big contribution. Consider the case of a denial of service attack, where a malicious entity attempts to make it impossible for users to access network services, generally by flooding the system with spurious requests for data both in user plane and control plane. In an Open RAN environment, when the local RAN begins to see a spike in “junk” data traffic or malware, it can detect the source of the attack can reconfigure its virtual firewall by way of dynamic service chaining and stop the attack on-the-fly by using edge-based AI analytics and intrusion detection system.
What are the Main Challenges to Open RAN Development?
Despite its promise, much work remains to be done to understand and close the technical gaps which stand in the way of the development and deployment of Open RAN technology. Here are a few of them:
- One challenge is reducing the latency which exists between the three parts of the disaggregated RAN, especially given the growing numbers of high-speed 5G users which will need to access it.
- While O-RAN offers a great deal of security opportunities, there are additional security challenges introduced due to orchestration, virtualization, slicing, and resource sharing that need to be investigated and mitigation techniques developed.
- Another challenge has to do with the use cases, traffic models, and deployment scenarios that Open RAN makes possible. There is a potential for confusion given that the various network interfaces used in these scenarios may adhere to different standards. Thus, the opening of these interfaces in an Open RAN environment could possibly impact the overall performance of the network and present interoperability issues.
- Another potential issue with Open RAN is that with a diversity of suppliers, fault- and configuration-management issues become larger and more difficult challenges to address, as do validation and testing, and ensuring compatibility with legacy 4G equipment.
Fast Tracking Open RAN Technology Development at IEEE SA
The IEEE SA Open RAN Industry Connections Program builds upon the previous work conducted by the O-RAN Alliance and the 3GPP Organization, and is focused on the many technical issues which need to be addressed in order for Open RAN solutions to be successfully developed and deployed.
An IEEE SA Industry Connections (IC) Program helps incubate new standards and related products and services in key areas where technologies fundamental to industry and society are changing rapidly. It facilitates collaboration among organizations and individuals in an open, neutral environment.
The IEEE SA Open RAN Industry Connection Program draws from and complements many other efforts at IEEE SA and at IEEE. The IEEE Future Networks Roadmap, for example, has laid a foundation for this project by way of developing a technology roadmap for 5G and beyond. Also, the IEEE 802.11™ Standard for Information Technology and its many amendments over the years have benefitted from the participation of volunteers from around the world who represent some of the leading technical minds in the industry. Other related work in this field is ongoing, such as a proposed standard known as Frugal 5G to specify an architecture for an affordable rural wireless broadband communication network.
This enables technologists to achieve consensus relatively quickly, and to produce content and other deliverables, which may include:
- Proof-of-concept use cases in collaboration with operators, vendors, end users, application service providers
- White papers, position papers, and peer-reviewed guides
- Publications in magazines and journals around Open RAN
- Conferences, webinars, workshops, and other events in collaboration with the industry, academia, and government
- Databases and registration services
- Software, tools, and web services
- Proposals for standards. When a need is seen for a new standard, a project authorization request (PAR) is created and, if approved, the standard then would be developed by an IEEE SA Working Group.
Learn More and Get Engaged
The IEEE SA Open RAN Industry Connection Program welcomes participants from academia, government, and industry such as telecommunications and network service providers, original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), technology providers, as well as stakeholders from other industry sectors.
Learn More and Join the Open RAN Industry Connections Program
Authors:
- Ashutosh Dutta, Ph.D., IEEE SA Open RAN Industry Connections (IC) Program Chair, IEEE Fellow, 5G Chief Strategist, Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Lab
- Purva Rajkotia, IEEE SA Connectivity & Telecom Practice Lead










Open RAN architectures will bring about more versatile, flexible, and resilient networks offering new features and capabilities, higher reliability, and greater security. Open RAN will offer network operators savings in operational costs and capital expenses, along with greater ease in implementing orchestration and closed-loop automation at the edge, and other new functions than is possible at present, such as dynamic resource scheduling, embedding detection, and mitigation techniques.