Procurement is emerging as a key area of impact for businesses as organizations increasingly seek to automate, optimize, and innovate their AI sourcing strategies. If organizations are considering adopting AI technologies, they should consider the importance of a responsible procurement and supply chain strategy.
AI-Driven Procurement: Laying the Foundation
Organizations can reap the substantial benefits of AI procurement in both material and human resources, particularly when taking guidelines into account. In an era where there are inherent challenges in managing the sheer amount of data generated, streamlining processes can help provide clearer paths forward. Efficiency and productivity rely heavily on quicker access to data to enable procurement processes with less friction.
That involves acquiring and integrating AI-driven technologies to automate routine tasks, leverage advanced analytics for decision-making, and improve overall efficiency. The process typically involves identifying needs, selecting solutions, implementing technologies, and continuous monitoring and optimization.
More Efficient Processes
AI can enhance procurement processes in numerous ways. For example, AI can automate invoice processing, reducing manual effort and feeding data into systems that enable data-driven decisions while driving compliance with evolving standards. This can lead to spend analysis that optimizes procurement strategies, helping organizations proactively adjust to market changes. Additionally, AI can detect fraudulent activity in procurement processes, enhancing security and compliance. AI bots can improve the customer experience by efficiently handling supplier inquiries, streamlining communication, and coordination.
AI procurement can also benefit various stakeholders within an organization by automating tasks, managing supplier relationships, and optimizing sourcing. Chief Procurement Officers (CPOs) leverage AI to develop strategy, manage risk, and align procurement practices with regulatory requirements. Finance departments use AI for spend analysis, cost optimization, and fraud detection. Supply chain managers can use AI to predict demand, manage inventory, and mitigate risks, while legal teams use it to handle contract management, compliance, and risk identification.
Addressing Guidelines and Standards
Guidelines in public procurement of AI are essential to address ethical considerations, reduce bias, and build trust through transparent AI decision-making. They emphasize the importance of using data ethically and securely, adhering to regulations, managing risks, and promoting sustainable practices.
IEEE 3119™ is the first standard of its kind to address AI procurement and is available for purchase on IEEE Xplore®.
IEEE 3119 aligns with global frameworks and standards such as the EU AI Act, NIST AI Risk Management Framework (RMF), Japan’s AI guidelines for Business, and ISO 42001, which collectively shape responsible AI governance.
IEEE 3119 is structured around six core procurement processes: Problem Definition, Solicitation Preparation, Vendor Evaluation, Solution Evaluation, Contract Negotiation, and Contract Monitoring. The addition of the “Solicitation Preparation” step is significant, as it helps procurement teams incorporate AI-specific requirements such as data transparency, governance maturity, and adaptability to evolving regulations.
IEEE 3119 addresses gaps in traditional procurement models and complements global efforts such as the EU AI Act and NIST AI RMF. These frameworks and standards promote ethical AI practices, privacy protection, and transparency.
Regulatory compliance offers a meaningful opportunity to build trust and transparency among stakeholders by identifying and mitigating AI deployment risks. Defining responsible AI procurement begins with strong consideration of transparency, accountability, and compliance with relevant standards. This approach supports more streamlined processes and operationally effective AI use that aligns with principles of fairness, ethical integrity, and long-term sustainability.
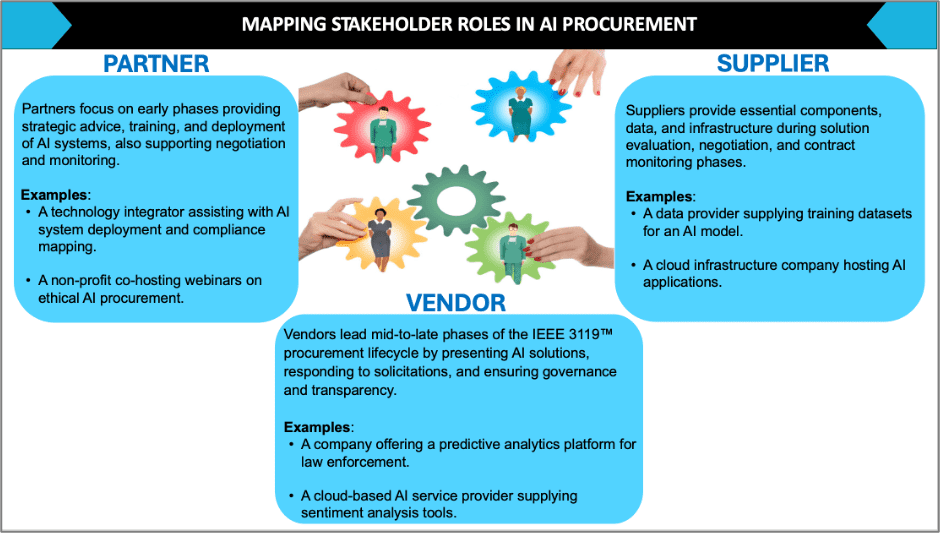
Mapping Stakeholder Roles in Responsible AI Procurement
The IEEE 3119 procurement lifecycle involves three key stakeholder groups: Partners, Vendors, and Suppliers – each contributing to different phases of responsible AI acquisition. Their roles are summarized below and visually represented in the diagram.
- Partners support early-stage activities like problem definition and solicitation preparation.
- Vendors lead mid-to-late phases by presenting AI solutions and ensuring transparency.
- Suppliers provide data, infrastructure, and components that influence system trustworthiness.
IEEE 3119 addresses gaps in traditional procurement models and complements global efforts such as the EU AI Act and NIST AI RMF. These frameworks and standards promote ethical AI practices, privacy protection, and transparency.
Regulatory compliance offers a meaningful opportunity to build trust and transparency among stakeholders by identifying and mitigating AI deployment risks. Defining responsible AI procurement begins with strong consideration of transparency, accountability, and compliance with relevant standards. This approach supports more streamlined processes and operationally effective AI use that aligns with principles of fairness, ethical integrity, and long-term sustainability.
Strategic Procurement with GenAI
The need for responsible procurement practices and adherence to standards also holds relevance in the evolving AI landscape of procurement operations because Generative AI (GenAI) has the potential to enhance how businesses manage complexity and risk. Envision a scenario where teams can collaboratively address supply chain challenges with the analytical precision of a seasoned investigator. Although these technologies are still maturing, GenAI can increasingly deliver real-time insights and predictive analytics that support more informed decision-making. These tools can assist in evaluating supplier credentials, anticipating potential disruptions, and reinforcing spending controls, thus contributing to operational continuity in both stable and uncertain conditions.
Imagine a future where creating requests for proposals (RFPs) and contracts becomes significantly more efficient through the support of GenAI by streamlining repetitive tasks. While these technologies are still evolving, they show promise in helping procurement teams improve spend categorization, demand forecasting, and supply chain visibility. When thoughtfully implemented, GenAI can support more strategic, data-informed decision-making.
This can also pave the way for automating key procurement processes like contract management and strategic sourcing, particularly through Machine Learning (ML) and Natural Learning Processing (NLP) technologies. While these tools are not yet universally plug-and-play, they are increasingly being used to reduce manual workloads, increase productivity, and improve competitiveness by streamlining repetitive tasks that often consume valuable time and resources.
Turning unstructured documents into structured data, especially when accuracy is important, holds significant promise. Although these capabilities are still evolving, real-time tracking and visibility drive up efficiencies by simplifying complex business operations. Enhancing transparency can support smoother operations and position organizations to realize profitability improvements over time.
Smart and Fast, Concise and Compliant
Effectively predicting market conditions and managing supplier relationships gives an organization a competitive advantage because it enables it to be more agile and responsive. GenAI is transforming the procurement paradigm by enabling smarter, faster, and more strategic operations. It’s not just about doing things better; it’s about reimagining what’s possible going forward.
However, organizations still face several challenges when adopting AI-driven procurement protocols. Fear and reticence can lead to resistance when new technologies usher in significant change that can ignite cultural evolution in the workplace. AI procurement is not a one-size-fits-all solution that applies uniformly to every business, but it is elaborate and flexible enough to cater to an organization’s requirements.
Since it is also growing in sophistication, handling increasing data loads necessitates finding new ways to deal with the deluge. Integrating new technology into an established system of well-defined applications and workflows can be complex and sometimes confusing. This only places a greater emphasis on investing in training to ensure a smoother transition.
Get Started with IEEE SA
Responsible AI procurement must be ethical, transparent, sustainable, accountable, and compliant. IEEE 3119 establishes guidelines for responsible AI procurement applicable to both public and private sector organizations that address vital considerations to help safeguard public benefit and well-being. Organizations that adopt these guidelines can navigate the complexities around deploying AI-driven applications, harnessing greater potential to achieve strategic goals and societal benefits.
If you’re interested in learning more about responsible AI procurement, you can check out the IEEE Responsible Procurement of AI training offered by IEEE SA. This training provides essential insights and practical guidance on IEEE 3119, helping organizations adopt ethical and effective AI procurement practices. It also introduces participants to a selection of key tools and rubrics from the standard.
Purchase the IEEE 3119 standard and enroll in the IEEE Responsible Procurement of AI training to equip your teams with tools to lead responsibly in the AI era.
This training is tailored for a wide audience, including mid-level procurement professionals, interdisciplinary team members, public and private sector buyers, non-procurement managers overseeing procurement functions, insurance carriers and AI vendors seeking to understand new transparency and disclosure expectations.
With AI redefining procurement, equipping teams with the tools and guidance is key to helping them stay ahead and maintain a competitive edge. This training offers a practical path forward for organizations committed to responsible, effective AI adoption.
Learn More About the IEEE Responsible Procurement of AI Training Today
Author: Usha Jagannathan, IEEE SA








